Blog
Xendoll has 22 years of experience in the production of small machine tools. We will help you choose the suitable machine and share our experience in CNC machining with you.
 Aug 28, 2025
Aug 28, 2025

 925
925
Bar feeding is an essential process in modern machining that improves efficiency, precision, and automation in turret lathes. For STEM educators and students using mini lathes, understanding bar feeding mechanisms—especially the role of feed rate—offers valuable insight into CNC technology and automated manufacturing. This article explores how bar feeding systems operate in turret lathes and why mini lathes are excellent tools for teaching these concepts in STEM environments.
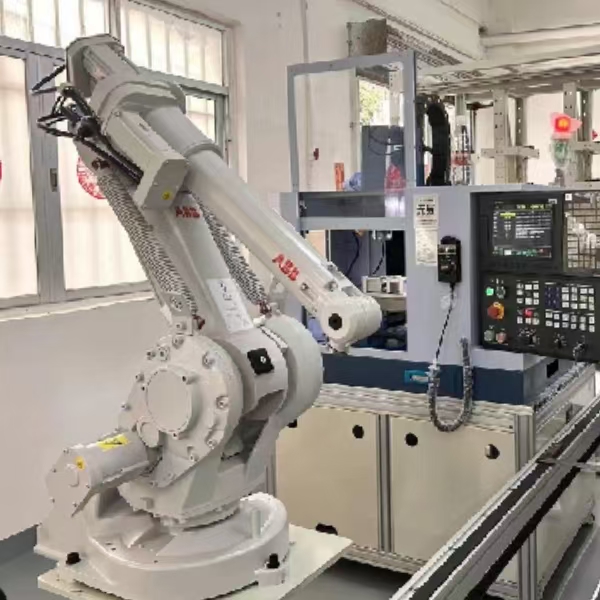

Bar feeders are auxiliary devices that automatically supply bar stock into a turret lathe, allowing continuous machining without frequent manual intervention. In a educational mini lathe context, simplified bar feeding can be demonstrated to show how automation works.
A typical bar feeder consists of a support frame, a feeding mechanism, and a controller. The bar stock is loaded into a tube, and when the lathe requires new material, the feeder pushes the bar forward to a predetermined length. This process is controlled based on the program running in the lathe, and the feed rate—the speed at which the bar is advanced—plays a critical role in ensuring consistent and accurate machining.
The heart of the system is the feeding mechanism, which can be mechanical, hydraulic, or servo-driven. In mini lathes used for STEM education, simpler mechanical or electronic feed systems are common. The feed rate must be calibrated according to the material type and desired cutting speed to avoid vibrations or breakage.
Modern bar feeders are seamlessly integrated with the lathe's CNC control system, functioning as a single, automated unit.In educational settings, students can learn programming basics by setting parameters such as the feed rate, which determines how quickly the bar is moved into the spindle.
Maintaining precise alignment is paramount to preventing bar deflection and safeguarding workpiece integrity during machining.Educators can use mini lathes to demonstrate how misalignment affects the finish of a part and how adjusting the feed rate can mitigate some of these issues.
Bar feeders include sensors and clutches to stop feeding in case of jams or overloads. This is especially important in classrooms, where safety is a priority.
Mini lathes offer a safe, accessible, and cost-effective way to introduce students to bar feeding automation. Here’s how they support STEM learning:
Hands-On Experience: Students can observe how feed rate influences machining quality and efficiency.
Programming Skills: By setting and adjusting parameters like feed rate, learners gain practical CNC programming experience.
Problem-Solving: Configuring a bar feeding system requires critical thinking about material properties, machine limits, and desired outcomes.
Career Preparation: Exposure to automation and precision machining prepares students for advanced training or careers in manufacturing.
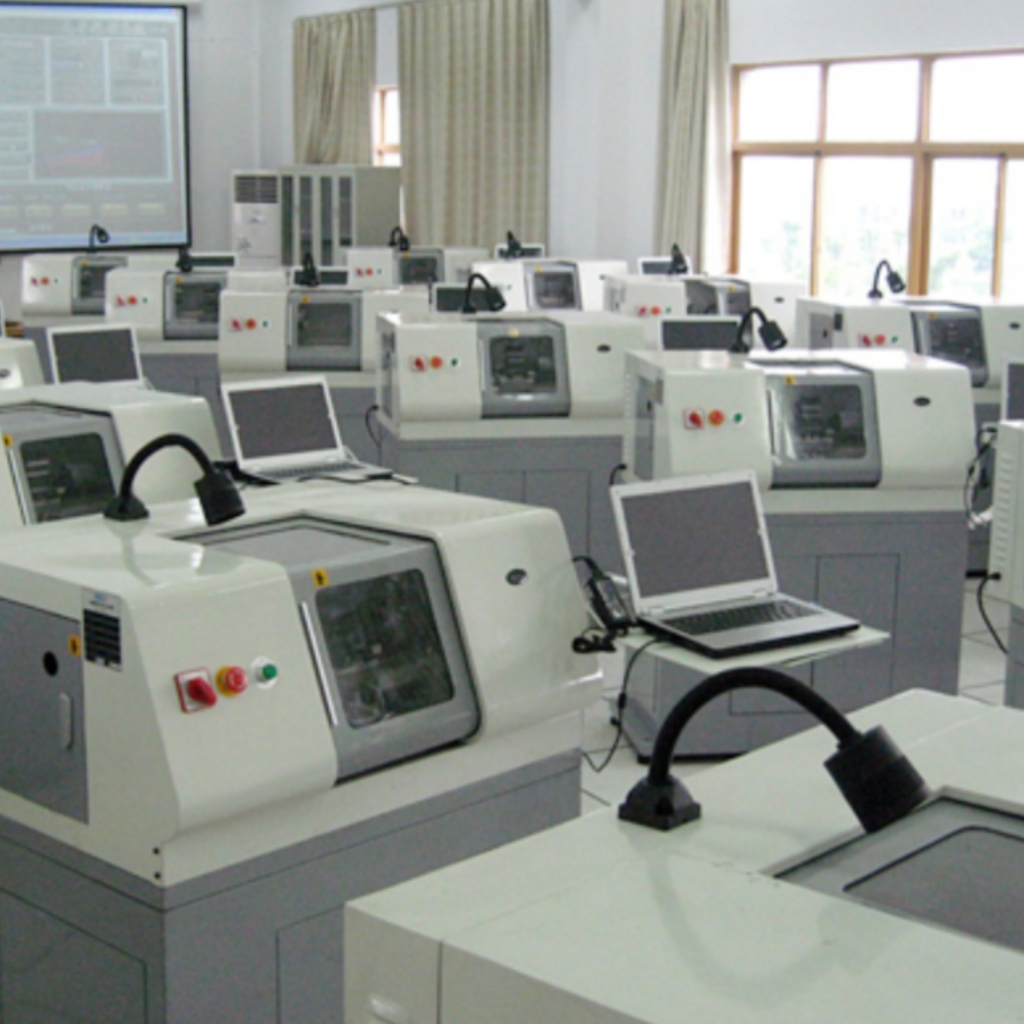

Understanding bar feeding in turret lathes—particularly the importance of feed rate—provides students with practical knowledge in automation, mechanics, and programming. Mini lathes, such as those from Xendoll Tools, serve as perfect educational platforms due to their safety, simplicity, and relevance to real-world applications. By integrating these concepts into STEM curricula, educators can inspire the next generation of engineers and technologists.
For more information about mini lathes suitable for STEM education, visit xendolltools.com.


 Show all our samples
Show all our samples
 Provide you with a free quote
Provide you with a free quote
 Answer all the questions you may have
Answer all the questions you may have
 Guided installation and other options
Guided installation and other options