Blog
Xendoll has 22 years of experience in the production of small machine tools. We will help you choose the suitable machine and share our experience in CNC machining with you.
 Aug 12, 2025
Aug 12, 2025
 XENDOLL
XENDOLL
 949
949
The translation of the small CNC milling machine operation tutorial :
I. Preparations Before Operation
1. Check the Machine Condition:
- Ensure that the power supply, air pressure, lubrication system, and other components of the CNC milling machine are in normal working condition.
- Check that all parts of the machine are intact, with no looseness or damage.
- Confirm that lubricating oil and cutting fluid are sufficient.
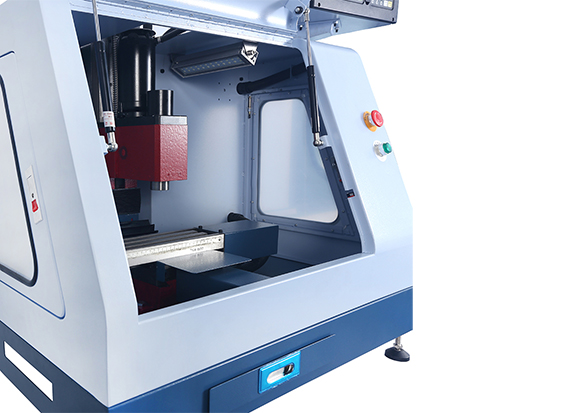
2. Prepare Tools and Workpieces:
- Check that the cutting tools are in good condition and select the appropriate tools to install on the spindle.
- Secure the workpiece firmly on the worktable, ensuring its position is accurate.
3.Check the Machining Program:
- Write or import the machining program and ensure it is error-free.
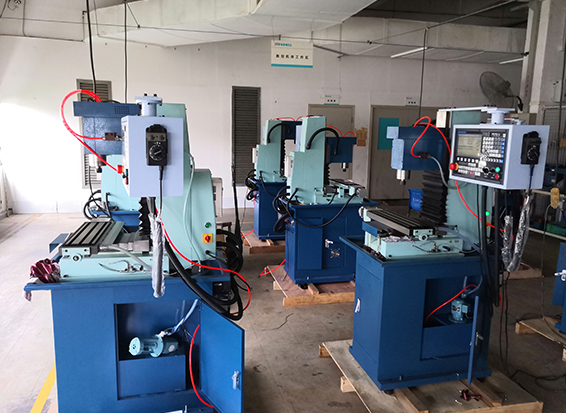

II. Power-On and Initialization
1. Power On:
- First, turn on the main power supply, then start the CNC system.
- Ensure the emergency stop button is released.
2. Return to Reference Point:
- After starting, return all axes (X, Y, Z) to the reference point to establish the machine coordinate system.
III. Program Input and Editing
1. Program Input:
- Input the machining program manually through the control panel or import it via external devices (such as a USB drive or network transfer).
- If the program is simple, it can be directly entered through the control panel.
2. Program Editing:
- If the program needs modification, switch to editing mode to add, delete, or modify it.
IV. Tool Setting and Parameter Adjustment
1. Tool Setting:
- Use a tool setter or manual tool setting to determine the initial position of the tool in the X, Y, and Z directions.
- Record the tool compensation values and enter them into the machine control system.
2. Parameter Adjustment:
- Set the spindle speed, feed rate, and other parameters according to the workpiece material and machining requirements.
V. Program Verification and Simulation
1. Program Verification:
- Lock the machine and run the program to check if the tool path is correct.
- If any issues are found, return to editing mode for modification.
2.Simulation Machining:
- Perform a simulation of the machining process on the machine control system to observe if the tool trajectory is reasonable.
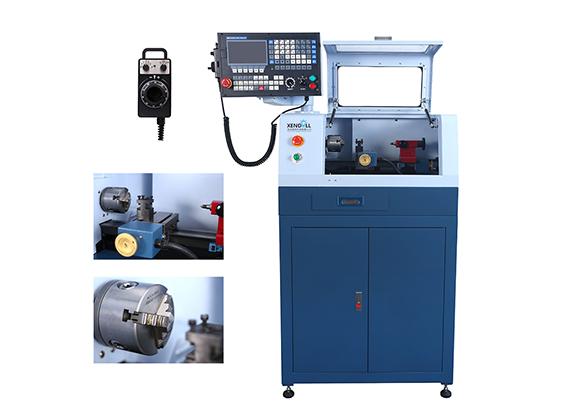

VI. Formal Machining
1. Start Machining:
- After confirming everything is ready, unlock the machine and start the machining program.
- Adjust the feed rate as needed during machining.
2. Monitor the Machining Process:
- Closely observe the machine's operation to ensure there are no abnormalities.
VII. Post-Machining Processing
1. Check the Workpiece:
- After machining is complete, check the workpiece dimensions and surface quality to ensure they meet requirements.
2. Clean the Machine:
- Remove chips and oil from the worktable.
3. Shut Down the Machine:
- First, turn off the CNC system, then shut down the main power supply.
VIII. Safety Precautions
1. Operational Safety:
- Wear appropriate protective gear while operating to avoid accidents.
- When manually moving the machine, ensure the Z-axis is at a safe height to prevent collisions between the tool and the workpiece.
2. Program Debugging:
- Always perform a trial run of the program before formal machining to prevent collisions between the tool and the workpiece.
3. Machine Maintenance:
- Regularly inspect the machine's lubrication and cooling systems to ensure they are functioning properly.
By following the above steps, you can safely and efficiently operate a small CNC milling machine. Always strictly adhere to the operating procedures to ensure machining quality and equipment safety.


 Show all our samples
Show all our samples
 Provide you with a free quote
Provide you with a free quote
 Answer all the questions you may have
Answer all the questions you may have
 Guided installation and other options
Guided installation and other options